The Best Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids Explained
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that are indispensable for maintaining your overall health. Let s explore the best sources of omega-3s together!
These powerful fats are crucial not just for heart and brain function but also for skin and joint health truly a cornerstone of your well-being.
You ll discover their numerous benefits, the recommended daily intake, and tips for seamlessly adding them into your diet, all while being mindful of potential risks.
Explore how omega-3s can significantly enhance your health!
Contents
- Key Takeaways:
- 1. Fish and Seafood
- 2. Plant-Based Sources
- 3. Fortified Foods
- 4. Supplements
- 5. Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- 6. Recommended Daily Intake
- 7. How to Incorporate Omega-3s into Your Diet
- 8. Potential Risks and Side Effects
- 9. Omega-3s and Heart Health
- 10. Omega-3s and Brain Function
- 11. Omega-3s and Eye Health
- 12. Omega-3s and Inflammation
- 13. Omega-3s and Joint Health
- 14. Omega-3s and Skin Health
- 15. Choosing the Best Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids for You
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What are omega-3 fatty acids and why are they important?
- What are the best sources of omega-3 fatty acids?
- How much omega-3 fatty acids should I consume per day?
- Are there any vegetarian sources of omega-3 fatty acids?
- Why are omega-3 fatty acids important for heart health?
- Can I take omega-3 supplements instead of getting it from food sources?
Key Takeaways:
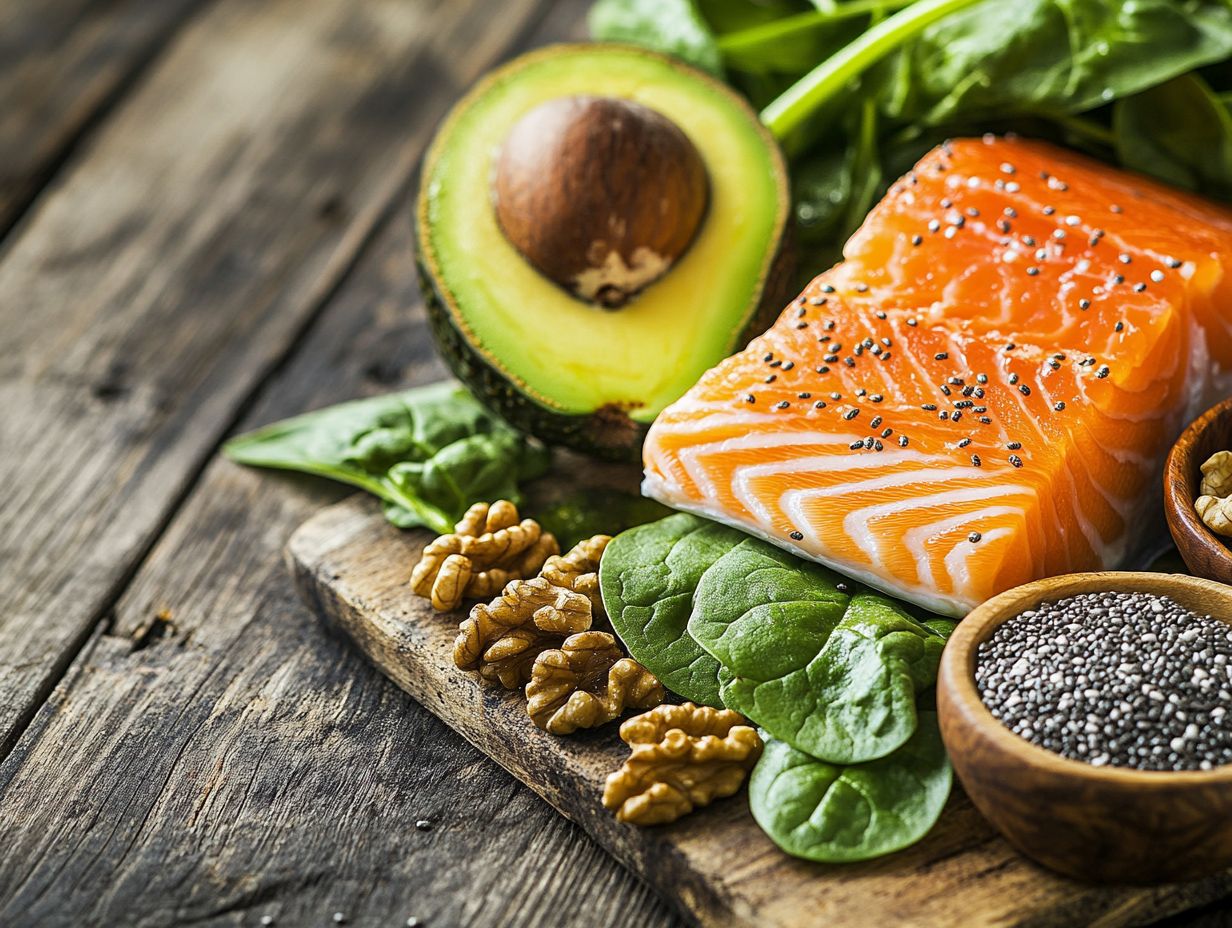

- Fish and seafood are the best sources of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly fatty fish like:
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Tuna
- Plant-based sources of omega-3s include chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts, but they may not be as readily absorbed by the body.
- Fortified foods like eggs and milk can also be good sources of omega-3s, but it’s important to check the label for the amount of added fatty acids.
1. Fish and Seafood
Fish and seafood are among the richest sources of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA and EPA. These nutrients play a crucial role in promoting heart health by reducing triglycerides and inflammation.
Some of the most beneficial types include:
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Sardines
These not only provide an excellent source of omega-3s but also deliver high-quality protein and essential vitamins. Research studies indicate that adding these fish to your diet can help lower cholesterol levels and enhance overall heart function.
Health organizations, including the Cleveland Clinic, recommend enjoying at least two servings of omega-3-rich fish each week to fully reap these benefits.
The impact of omega-3s extends beyond heart health. They re also linked to improved brain function and a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
This reinforces the importance of including these nutrient-rich foods in your healthy lifestyle.
2. Plant-Based Sources
Plant-based sources of omega-3 fatty acids, especially ALA found in flaxseed, chia seeds, and walnuts, offer a superb alternative for enhancing your intake of healthy fats without relying on fish or seafood.
These nutrient-dense foods not only provide essential fatty acids but also come packed with a variety of vitamins and minerals. Incorporating them into your daily meals is easy; simply add a couple of tablespoons of ground flaxseed to your smoothies or oatmeal, sprinkle chia seeds on your yogurt, or munch on a handful of walnuts as a snack.
By prioritizing ALA-rich foods, you can actively support your cardiovascular health, which is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart and reducing inflammation in your body.
3. Fortified Foods
Fortified foods have gained significant popularity as a way to elevate your omega-3 intake, incorporating essential fatty acids such as DHA and EPA into everyday products like eggs, yogurt, and milk to meet various dietary needs.
You ll also discover fortified options like bread and cereals enriched with omega-3s, making it simpler than ever to weave these crucial nutrients into your diet. Nutrition labels now proudly highlight the specific omega-3 content, giving you the power to make informed choices about your daily consumption.
This is especially advantageous for those who may find it challenging to include fatty fish or other traditional sources rich in omega-3s, such as walnuts or flaxseeds, in their meals.
By embracing fortified foods, you can bolster your heart health, enhance cognitive function, and potentially diminish inflammation, all while indulging in familiar and convenient products. Start adding these to your diet today for a healthier tomorrow!
4. Supplements
Omega-3 supplements, including well-known options like cod liver oil and fish oil capsules, provide a convenient way to ensure you’re getting enough essential fatty acids. These fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, are crucial for your overall health and well-being.
You ll find these supplements in various forms, such as krill oil or algae-based options tailored for vegetarians. Each offers different omega-3 levels and specific health benefits. Research suggests that a daily intake of 250 500 mg of combined EPA and DHA can support heart health, enhance cognitive function, and reduce inflammation.
When selecting supplements, seek out high-quality products that have undergone third-party testing for purity. This ensures they re free from contaminants, like heavy metals. Consult recommendations from reputable health organizations to choose the most suitable supplement for your health goals.
5. Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids

Omega-3 fatty acids offer an impressive array of health benefits that you simply can t overlook. They help reduce inflammation, support heart health, and enhance brain function, making them vital for warding off chronic diseases.
For cardiovascular health, omega-3s are essential. They lower triglyceride levels, reduce blood pressure, and improve heart rhythm. Research in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology shows that regular consumption of omega-3s significantly diminishes the risk of heart disease due to their powerful anti-inflammatory properties.
Omega-3 fatty acids are equally crucial for brain function. They play a pivotal role in developing and maintaining neural structures. Studies indicate they may enhance cognitive functions and slow cognitive decline in older adults. Recent research emphasizes the connection between omega-3 intake and a lowered risk of Alzheimer s disease, suggesting these fatty acids protect against neurodegeneration.
This protective effect stems from their ability to promote neuronal plasticity and reduce oxidative stress, contributing to better brain health as you age.
6. Recommended Daily Intake
Health organizations recommend maintaining a daily intake of omega-3 fatty acids for optimal health. It’s important to consume both EPA and DHA, ideally through your diet and/or supplements.
For adults, the typical recommended dosage is around 250 to 500 milligrams per day. Pregnant or nursing individuals might benefit from slightly higher amounts, often suggested at 200 to 300 milligrams. The American Heart Association advises individuals with heart disease to aim for about 1,000 milligrams daily. Keep in mind that age and individual health conditions can influence these recommendations. If you’re over 50, you may need to boost your intake due to changing metabolic needs.
To meet your omega-3 requirements, consider incorporating fatty fish such as:
Fatty Fish Sources
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Sardines
into your meals, or opt for plant-based sources like:
Plant-Based Sources
- Flaxseeds
- Chia seeds
- Walnuts
If dietary adjustments aren’t effective, high-quality fish oil or algal oil supplements may offer an effective alternative. Act now to boost your omega-3 intake!
7. How to Incorporate Omega-3s into Your Diet
Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into your diet can be effortless. There are many omega-3 foods packed with healthy fats that enhance the flavor and nutrition of your meals.
With just a few mindful adjustments, you can easily boost your omega-3 intake. For instance, tossing a tablespoon of flaxseed into your morning smoothie or oatmeal amps up the nutritional profile and adds a delightful nutty nuance.
When planning your dinners, think about opting for fatty fish like salmon or sardines. Grilling or baking them with a sprinkle of herbs can transform a simple meal into a delicious dish.
You can also whip up snack options like chia seed pudding or roasted walnuts, which fit seamlessly into your daily routine. By embracing these delicious and practical ideas, you can cultivate a more omega-3-rich diet that supports your overall health.
8. Potential Risks and Side Effects
While omega-3 fatty acids offer a wealth of health benefits, stay aware of potential risks and side effects that come with their consumption, especially regarding supplements and the risk of mercury poisoning from certain fish.
For example, you might experience gastrointestinal issues such as bloating or diarrhea when taking omega-3 supplements, particularly in high doses. Remember, not all fish are created equal; larger predatory species like tuna can accumulate harmful levels of mercury over time.
Therefore, it’s wise to select your omega-3 sources carefully, favoring smaller fish such as sardines or anchovies, which are generally lower in mercury. By sticking to recommended dosages, you can help minimize side effects and enjoy the health benefits of omega-3s without unnecessary risks.
9. Omega-3s and Heart Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are key players in maintaining your heart health. They have been shown to lower triglycerides, improve cholesterol levels, and support the overall function of your cardiovascular system, ultimately reducing your risk of heart disease.
Research indicates that these essential fats can enhance endothelial function, leading to better blood flow and reduced inflammation within your blood vessels. Numerous studies have demonstrated the protective effects of dietary sources, such as fatty fish, and supplements like fish oil, which provide high concentrations of these beneficial acids.
By ensuring regular intake, you can maintain optimal levels over time, contributing to a healthier cardiovascular profile. Experts recommend integrating omega-3s into your daily nutrition not just to promote heart health but also to enjoy long-term benefits. Consistency in consumption is vital for reaping these rewards.
10. Omega-3s and Brain Function

The consumption of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), is linked to enhanced brain function. Research indicates that these essential nutrients play a crucial role in cognitive health and may even help reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
DHA is vital for maintaining the integrity of cell membranes in your brain, facilitating effective communication between neurons. Studies have shown that individuals with higher levels of DHA often exhibit improved memory retention and mental clarity. Research published in various peer-reviewed journals highlights that omega-3 supplementation may support neuroprotection, helping to shield your brain cells from damage.
An adequate intake of these fatty acids has been correlated with improved mood regulation, underscoring their significance not only for memory but also for your overall mental well-being. This growing body of evidence reinforces the importance of incorporating sources of omega-3s into your diet for optimal cognitive health.
11. Omega-3s and Eye Health
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA, are essential for your eye health, contributing to optimal vision and offering protection against conditions like macular degeneration.
Research has revealed that these vital fats play a significant role in supporting the structure and function of your retina, which is crucial for clear sight.
People who eat more omega-3s have a lower risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Omega-3s also help reduce dry eye syndrome, a common issue as we age.
By incorporating omega-3-rich foods such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts into your diet, you can enhance your eye health and potentially ward off degenerative diseases associated with aging.
12. Omega-3s and Inflammation
Omega-3 fatty acids are celebrated for their remarkable anti-inflammatory properties, making them a valuable ally in managing chronic inflammation and reducing the risk of various chronic diseases.
Extensive research has consistently shown that these essential fats, prevalent in fatty fish and flaxseeds, play a crucial role in helping your body manage inflammation. Increasing your omega-3 intake may offer relief if you suffer from conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, or even cardiovascular issues.
Omega-3s help produce anti-inflammatory molecules that can significantly alleviate symptoms and enhance your overall health. For example, one study revealed that patients with rheumatoid arthritis experienced reduced joint pain and stiffness after incorporating omega-3 supplements into their regimen, highlighting their potential as a therapeutic option.
13. Omega-3s and Joint Health
The anti-inflammatory effects of omega-3 fatty acids can significantly enhance your joint health, easing symptoms related to conditions like arthritis and boosting your overall mobility.
Research shows that these essential fats, primarily sourced from fish oil and select plants, play a crucial role in modulating your body’s inflammatory response. Clinical studies reveal that individuals who increased their omega-3 intake experienced notable reductions in joint stiffness and pain transformative outcomes for those grappling with chronic issues.
Regular consumption of omega-3s has been associated with improved joint function, indicating that you could enjoy a better quality of life. Given these promising benefits for joint health, it s essential for those dealing with arthritis and similar challenges to consider adjusting their diets or supplementation strategies accordingly.
14. Omega-3s and Skin Health
Want to boost your skin health? Omega-3 fatty acids are key! They hydrate your skin and help tackle conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
These essential fats work by fortifying your skin’s barrier, which helps retain moisture and protects against environmental stressors things like pollution or UV rays that can harm your skin. Research indicates that a diet rich in omega-3s can significantly decrease inflammatory markers in your body, leading to fewer flare-ups of skin disorders.
If you re aiming to improve your skin texture and resilience, incorporating foods such as:
- Fatty fish
- Walnuts
- Flaxseeds
into your meals is an excellent approach. Plant-based eaters can consider fish oil or algae oil supplements. Staying hydrated and avoiding too much sun will also help your skin.
15. Choosing the Best Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids for You

Choose the best sources of omega-3 fatty acids carefully. Consider your dietary needs and preferences. Whether you prefer fish, plant-based sources, or fortified foods, ensure that your diet provides adequate omega-3 content.
Evaluating these options extends beyond merely listing types of food; it involves a keen examination of any food allergies or preferences you may face, such as seafood allergies or a commitment to veganism. Your health goals shape your choices. If heart health is your focus, you might prefer fatty fish like salmon. Meanwhile, those looking to reduce inflammation may find flaxseeds or chia seeds more beneficial.
Striking a balance in omega-3 intake from these diverse sources is crucial for reaping optimal health benefits. This approach enriches your nutrient profile and allows you to meet your individual needs without sacrificing your personal choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are omega-3 fatty acids and why are they important?
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of healthy fat that our bodies need to function properly. They are essential for our brain and heart health and can also help reduce inflammation in the body.
What are the best sources of omega-3 fatty acids?
The best sources of omega-3 fatty acids include:
- Fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, and mackerel
- Plant-based foods like chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts
How much omega-3 fatty acids should I consume per day?
The recommended daily intake of omega-3 fatty acids is 250-500 milligrams. This can easily be achieved by eating 2-3 servings of fatty fish per week or incorporating plant-based sources into your meals.
Are there any vegetarian sources of omega-3 fatty acids?
Yes, there are several vegetarian sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Some examples include:
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds
- Hemp seeds
- Walnuts
These sources contain a type of omega-3 called alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which can be converted into the more beneficial forms of omega-3s, EPA and DHA, in the body.
Why are omega-3 fatty acids important for heart health?
Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to lower triglyceride levels, reduce blood pressure, and decrease the risk of heart disease. They also have anti-inflammatory properties that can improve overall heart health.
Can I take omega-3 supplements instead of getting it from food sources?
While omega-3 supplements can be beneficial, it is always best to get nutrients from whole food sources. Supplements may not provide the same health benefits as whole foods and may also contain other ingredients that could be harmful. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplements.
Start incorporating omega-3 sources into your diet today for better health!